Introduction
- The allure of classic cars
- Why understanding the birth of the automobile is key to appreciating their legacy
2. Early Concepts of the Automobile
- Pre-car innovations and how the idea of a “vehicle” emerged
- Early forms of self-propelled transportation
3. The First Successful Automobile: Karl Benz’s Creation
- The 1885 Benz Patent-Motorwagen
- How this marked a turning point in transportation
- Innovations of Karl Benz and their lasting impact
4. The Rise of Automobile Manufacturers
- The birth of early car companies like Peugeot and Daimler
- How they influenced the automotive world
5. Early Car Models and Designs
- The development of the first car designs and their characteristics
- Differences between early models and modern cars
6. Mass Production Revolutionized by Henry Ford
- The introduction of assembly lines and mass production
- How Ford made automobiles affordable to the masses
7. The Influence of Early Automobiles on Society
- How the automobile began to change daily life
- Social and cultural impacts
8. The Evolution of Classic Cars Over the Decades
- How design and technology progressed through the 20th century
- The emergence of iconic models and the rise of car culture
9. World Wars and Their Impact on Automobile Development
- How both World Wars influenced car technology
- Post-war advancements and the birth of car brands like Chevrolet and Ferrari
10. The Classic Car Era: Post-War Golden Age
- The 1950s to 1970s as the golden age of classic cars
- Iconic cars from this era and their legacy
11. What Makes a Car “Classic”?
- Defining characteristics of a classic car
- How different cultures view classic cars
12. Classic Cars in Modern Times: From Vintage to Investment
- The modern appreciation for classic cars
- How classic cars have become valuable collectibles
13. The Future of Classic Cars
- Where the classic car industry is headed
- The role of technology and sustainability in classic car preservation
14. Conclusion
- Reflecting on the journey of the automobile from its humble beginnings
- The lasting legacy of classic cars
FAQs
- What is considered the first car ever made?
- How did Karl Benz contribute to the birth of the automobile?
- When did mass production of cars begin?
- Why are classic cars considered valuable?
- Will classic cars continue to be relevant in the future?
The Birth of the Automobile: How Classic Cars Began
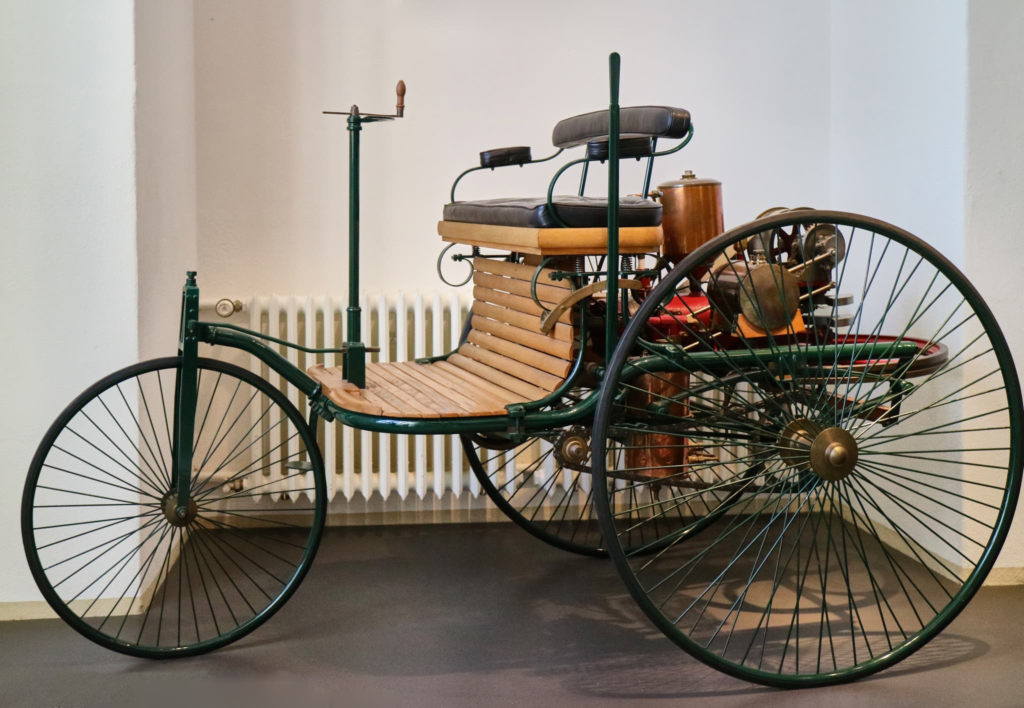
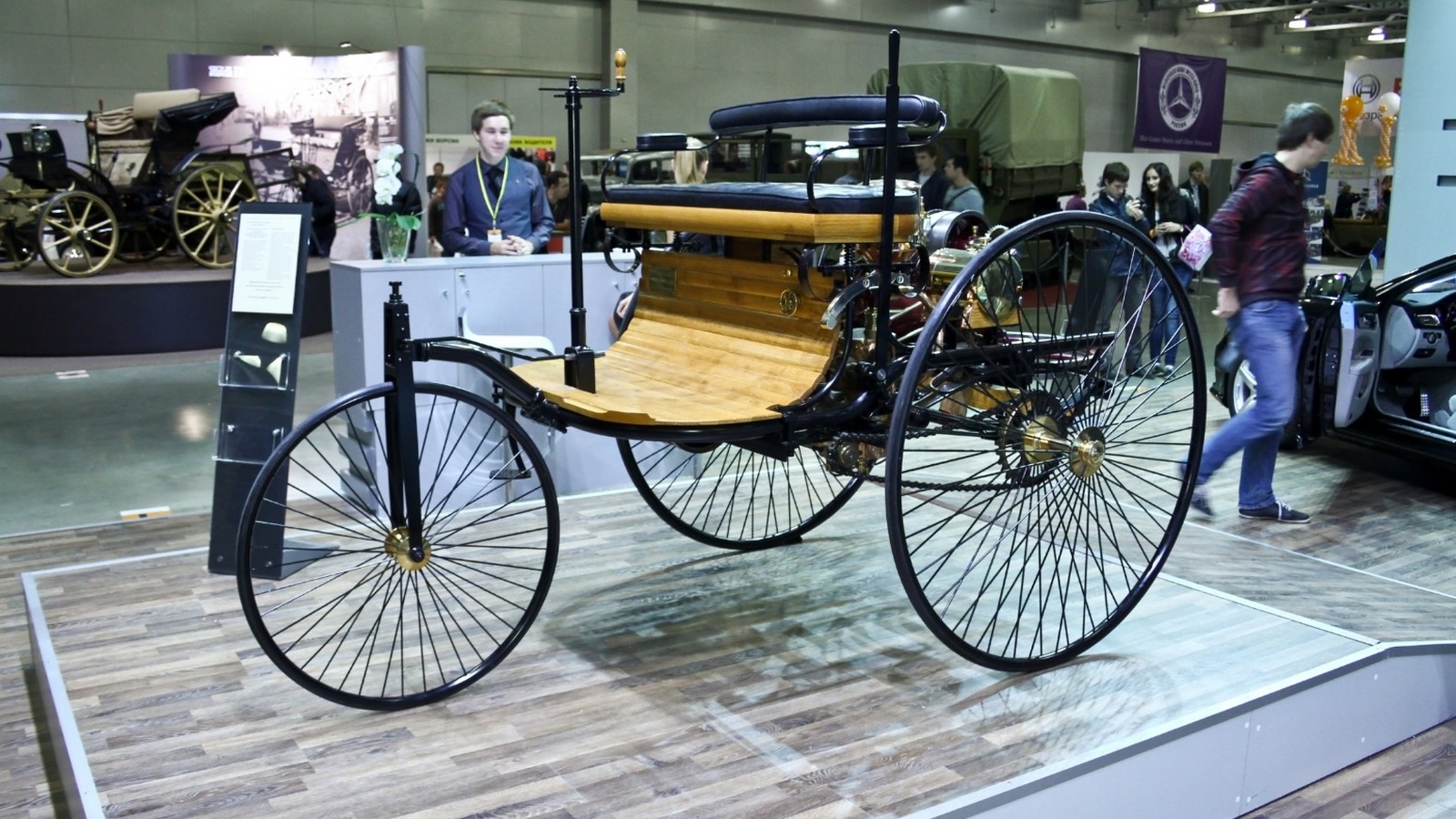
Classic cars have an undeniable charm, drawing enthusiasts from all corners of the globe. But have you ever wondered how the automobile—these iconic machines—came into being? Understanding the birth of the automobile not only gives us insight into how far we’ve come but also explains why classic cars are so revered today.
Early Concepts of the Automobile
The idea of a vehicle that could move on its own without horse power dates back centuries. While humans have long dreamed of mechanical transportation, the first practical self-propelled vehicle emerged in the late 19th century. Before that, there were early concepts, such as steam-powered wagons, which sparked the imagination of inventors. But it wasn’t until various technological breakthroughs were combined that the automobile as we know it was born.
The First Successful Automobile: Karl Benz’s Creation
Fast forward to 1885, when a German inventor named Karl Benz developed the world’s first practical automobile, the Benz Patent-Motorwagen. This vehicle, powered by an internal combustion engine, is considered the true birth of the modern car. It wasn’t just about inventing a machine that moved; it was about creating something functional and sustainable. Benz’s vehicle was powered by gasoline and had a surprisingly modern feel for its time. With three wheels, a wooden chassis, and a top speed of just 10 miles per hour, it was far from a sleek sports car. But its importance cannot be overstated—it marked the beginning of the automotive era.
The Rise of Automobile Manufacturers
As the 1880s turned into the 1900s, the potential of the automobile began to capture the attention of other inventors and entrepreneurs. Peugeot in France and Daimler in Germany were among the earliest companies to produce cars. Their efforts helped lay the foundation for the modern auto industry. These early carmakers were instrumental in proving that automobiles could be more than just experimental machines—they could be mass-produced and used in everyday life.
Early Car Models and Designs
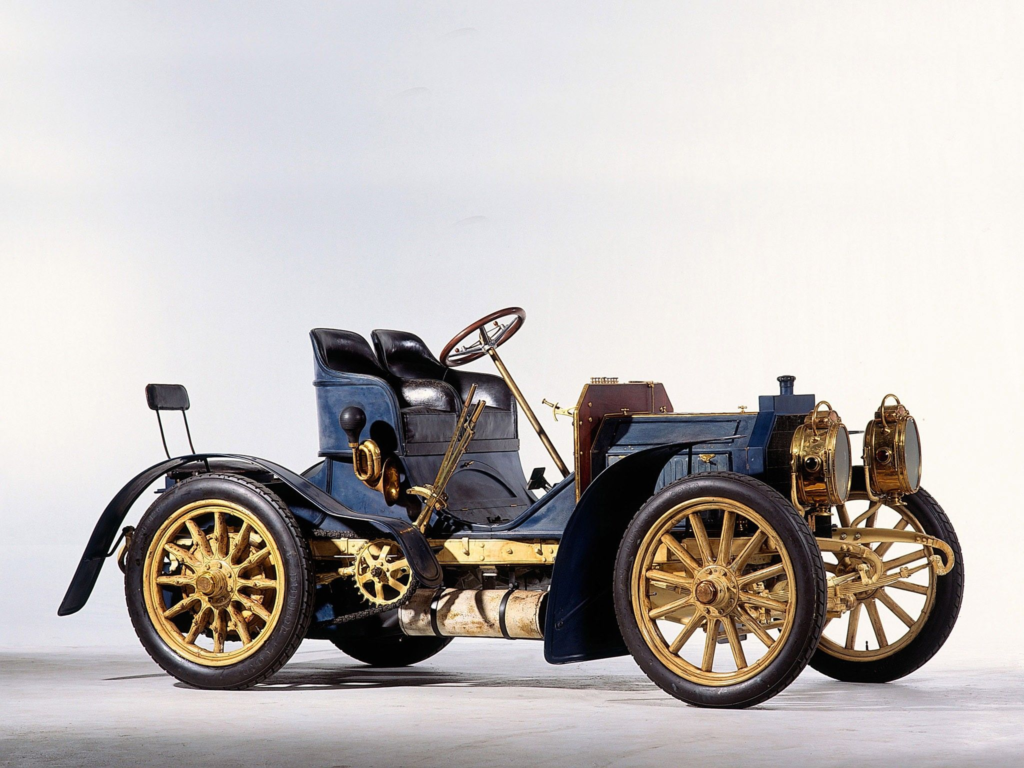

The first cars looked nothing like today’s sleek, aerodynamic vehicles. Early car designs were often bulky, wooden affairs with exposed mechanical parts. Some early models had enormous wheels, while others sported large engines visible on the outside. Over time, however, cars became more refined. Innovations such as electric starters, rubber tires, and improved engines helped enhance their performance and usability. By the 1920s, the car was no longer just a luxury for the rich; it was a symbol of independence and freedom for the masses.
Mass Production Revolutionized by Henry Ford
In 1908, Henry Ford introduced the Model T, a car that changed the automotive industry forever. The Model T was affordable, reliable, and simple to maintain. Ford revolutionized the manufacturing process by introducing the assembly line. This allowed for the mass production of cars, making them accessible to everyday people. By 1927, Ford had produced over 15 million Model Ts, cementing the automobile’s place in mainstream society.
The Influence of Early Automobiles on Society
The rise of the automobile didn’t just change how people traveled—it changed society itself. People could now travel longer distances in a fraction of the time. The concept of the road trip was born, and it wasn’t long before communities began to grow around automotive technology. Rural areas were no longer isolated, and people’s perceptions of distance changed. Cars symbolized freedom and self-sufficiency, and their growing accessibility opened doors to social mobility.
The Evolution of Classic Cars Over the Decades
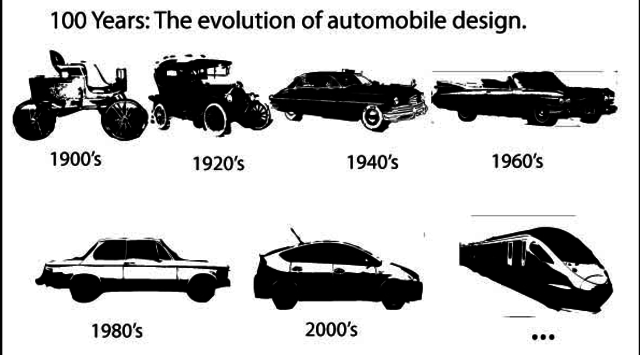
From the 1920s onward, the design of cars evolved dramatically. Automobiles became faster, more powerful, and, perhaps most importantly, more stylish. By the 1930s, brands like Chrysler and Cadillac were turning out models that were true works of art. Streamlined bodies, sleek curves, and powerful engines defined this era.
As the decades wore on, cars became even more advanced. The 1950s and 1960s saw the rise of iconic muscle cars, like the Chevrolet Corvette and the Ford Mustang, which are now considered prime examples of classic cars. The technology, aesthetics, and engineering from this period laid the groundwork for today’s car culture and gave birth to the classic car as we know it.
World Wars and Their Impact on Automobile Development
Both World War I and World War II had a profound impact on the automobile industry. During these times, automobile manufacturers shifted gears to focus on producing military vehicles. This period saw significant advancements in engineering, which eventually found their way into civilian cars. After the wars, car companies returned to producing consumer vehicles, with new technologies and designs that reflected the changes in global industry and engineering.
The Classic Car Era: Post-War Golden Age
The post-war era, especially from the 1950s to the 1970s, is often referred to as the golden age of classic cars. This period produced some of the most iconic cars in history, including the Chevrolet Corvette, Jaguar E-Type, and Ferrari 250 GTO. These cars combined cutting-edge technology with beautiful design, resulting in cars that are still celebrated and highly sought after by collectors today. The enthusiasm for cars during this period helped foster the car culture we see today.
What Makes a Car “Classic”?
So, what makes a car “classic”? A classic car is typically defined as a vehicle that is at least 20 to 25 years old and holds some degree of historical significance. Whether it’s the design, performance, or rarity, classic cars are prized for their unique characteristics. The term also evokes a sense of nostalgia, as many of these cars represent an era of innovation, luxury, and a sense of adventure.
Classic Cars in Modern Times: From Vintage to Investment

Today, classic cars are not just symbols of automotive history; they’ve become valuable collectibles and investments. Auctions dedicated to classic cars have exploded in popularity, with some rare models selling for millions of dollars. Modern-day enthusiasts seek out classic cars not just for their beauty but for their potential financial value. Owning a classic car has become a prestigious hobby for many, with collectors pouring money into restoring and maintaining these historical treasures.
The Future of Classic Cars
While modern technology continues to change the automotive industry, the future of classic cars remains bright. As electric cars and autonomous vehicles become more prevalent, many classic car owners are focused on preserving the heritage and legacy of their vehicles. The challenge will be ensuring that these cars remain roadworthy in an era dominated by technology-driven change, while also maintaining their status as beloved pieces of automotive history.
Conclusion
The birth of the automobile is a tale of innovation, persistence, and ingenuity. From the earliest ideas of self-propelled vehicles to the mass production of cars that changed society, the automobile industry has come a long way. Classic cars, in particular, represent a golden era of design, craftsmanship, and technological advancement. As we look to the future, the legacy of these vehicles will continue to inspire admiration and awe.
FAQs
- What is considered the first car ever made?
The Benz Patent-Motorwagen, created by Karl Benz in 1885, is often considered the first practical car. - How did Karl Benz contribute to the birth of the automobile?
Benz developed the first gasoline-powered car, which introduced the concept of the modern automobile. - When did mass production of cars begin?
Mass production began with Henry Ford’s introduction of the Model T in 1908 and the use of the assembly line. - Why are classic cars considered valuable?
Classic cars are valued for their rarity, historical significance, and often their design and performance. Many classic cars have appreciated in value over time. - Will classic cars continue to be relevant in the future?
While the future of the automobile is changing with electric and autonomous vehicles, the classic car market remains strong due to the continued appreciation for vintage automobiles.
